A solar system comprises of several major components, each critical to its normal function. See below for high level detail about these components, and their role in the wider solar system.
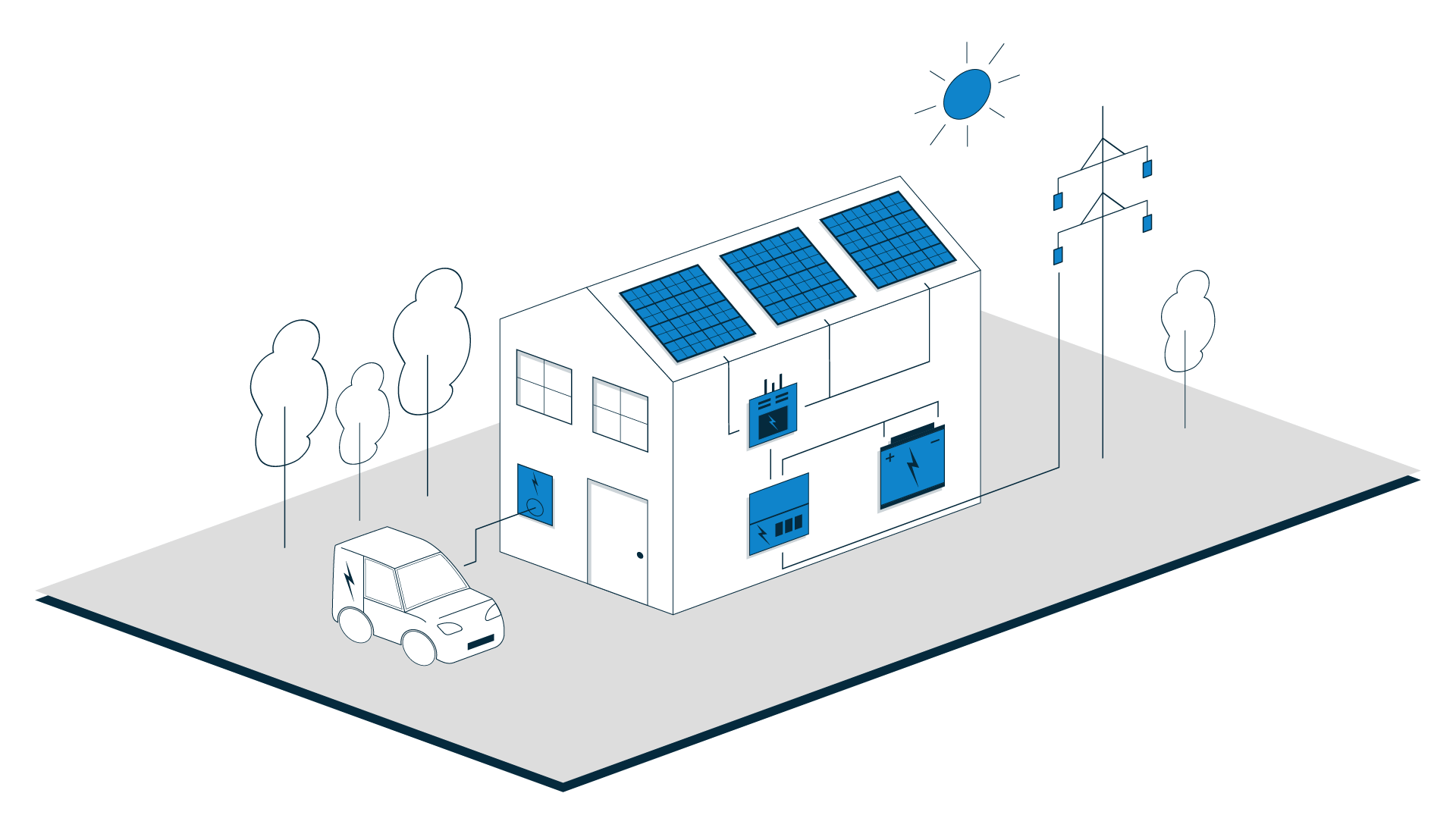
Our sun, the most abundant source of natural energy known to mankind. At ground level, the available photon energy is around 960W per m^2. With an average panel efficiency, this means around 192W per m^2 is up for grabs.
The solar array - the array captures the suns photons, inducing an electrical potential across the solar cells by leveraging the 'photoelectric' effect - an electrical current starts to flow.
The inverter converts DC electrical energy from the array into AC electrical energy. This is used in our homes and offices and is 'matched' to the grid supply provided by your energy supplier.
This is where all of your 'final circuits' terminate to the grid supply - sometimes referred to as the 'fuse board'. We'll need to connect your inverter to this with a new circuit to enable you to export electrical energy and provide constant power to the inverter.
These sophisticated batteries play a pivotal role in capturing surplus energy during periods of low demand, ensuring it's available for consumption during peak times or when solar production is diminished, such as in the evenings or at night.
This is where electrical energy is imported from the grid to service your property. It is also where any excess electrical energy that can't be used is distributed . E.g. if there is no ESS system, or the ESS system is full. A well specified system will reduce your demand considerably and save you money on your bills.
Energy diverted to your electric vehicle on demand or scheduled.
The Energy Source
Our sun, the most abundant source of natural energy known to mankind. At ground level, the available photon energy is around 960W per m^2. With an average panel efficiency, this means around 192W per m^2 is up for grabs.
The solar array
The solar array – the array captures the suns photons, inducing an electrical potential across the solar cells by leveraging the ‘photoelectric’ effect – an electrical current starts to flow.
Inverter
The inverter converts DC electrical energy from the array into AC electrical energy. This is used in our homes and offices and is ‘matched’ to the grid supply provided by your energy supplier.
The Nation Grid
This is where electrical energy is imported from the grid to service your property. It is also where any excess electrical energy that can’t be used is distributed . E.g. if there is no ESS system, or the ESS system is full. A well specified system will reduce your demand considerably and save you money on your bills.
Energy storage system (ESS)
These sophisticated batteries play a pivotal role in capturing surplus energy during periods of low demand, ensuring it’s available for consumption during peak times or when solar production is diminished, such as in the evenings or at night.
Consumer unit
This is where all of your ‘final circuits’ terminate to the grid supply – sometimes referred to as the ‘fuse board’. We’ll need to connect your inverter to this with a new circuit to enable you to export electrical energy and provide constant power to the inverter.
EV charger
Energy diverted to your electric vehicle on demand or scheduled.



